In industries such as paints, coatings, textiles, and pharmaceuticals, getting the interaction between liquid and solids precisely right can make a significant impact on product performance and quality.
Among the many additives used to achieve wetting and dispersing agents are two of the most important additives that achieve this interaction.
Table of Contents
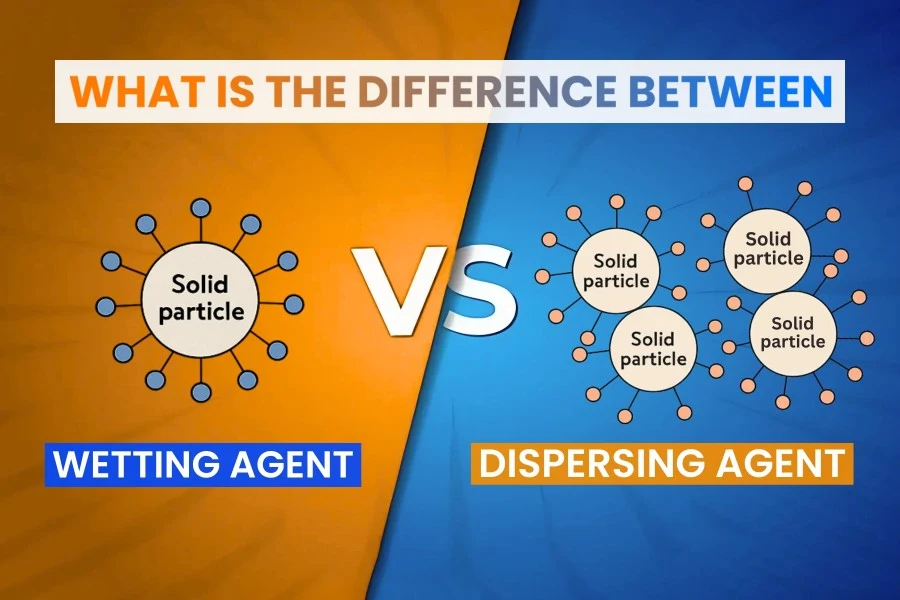
Both sound similar, but they are fundamentally different, and each serves a different purpose. A dispersing agent breaks down solid particles and creates stability of solids in a liquid medium to maintain a homogeneous dispersion.
They are typically used to stabilize pigments, minerals, or any other fine particles that need to be distributed homogeneously in a liquid formulation, while a wetting agent only reduces a liquid’s surface tension so that it can penetrate a surface more effectively or be spread more easily.
Understanding the difference between dispersing agent and wetting agent is important for many industries interested in smooth application and consistent color, or uniformity of particle distribution. Let’s examine these definitions more closely and discuss their uses and how they work!
What is a Dispersing Agent?
A dispersing agent is a chemical additive that helps separate solid particles and distribute them in a liquid medium. If a dispersing agent is not used, solid particles will tend to agglomerate or lump together, lose stability, and sink to the bottom of the liquid phase, causing inconsistent quality and performance.
Roles of a Dispersing Agent
Dispersing agents: Dispersing agents are designed to,
-break up particle clusters and impede particle re-agglomeration.
-stabilize suspensions to create a uniform mixture.
-improve color strength and consistency for paints, coatings, and inks.
-reduce waste by inhibiting sedimentation and re-agglomeration.
-promote application performance by providing an even coating.
Dispersing agents have a wide range of applications across many industries:
Paints & Coatings – To disperse pigments consistently to ensure color uniformity.
Pharmaceuticals – To ensure active ingredients are even throughout liquid formulations.
Textiles – To allow dye to penetrate evenly for consistent coloring.
Ceramics – To prevent particle clumping in ceramic slurries.
Adhesives & Sealants – To stabilize fillers and improve bonding performance.
What are the Key Chemicals in Dispersing Agents?
There are many different chemicals; we will list a couple of the chemicals that are extremely common in dispersing agents. A chemical that is widely used for its excellent dispersion properties, stability, and heat stability is 2-acrylamido-2-methyl propane sulfonic acid (AMPS monomer).
Another common compound is 15214-89-8, which offers good performance reliability for all the industrial dispersing agent applications.
As an interesting example, one of our products is Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), a versatile compound used in drilling fluids to help keep clay in suspension and therefore improve drilling efficiency.
What is a Wetting Agent?
A wetting agent is a substance that is used to reduce the surface tension of a liquid, giving it an easier and quicker spread over a solid substrate.
Think of it this way: The wetting agent is a “helping hand” to impart liquid equilibrium on surfaces and permeate porous structures.
Functions of a Wetting Agent:
- Decrease surface tension to enhance penetration.
- Improve spreading for uniform coverage.
- Increases adhesion to solid surfaces.
- Increase absorption in porous materials.
- Helps to facilitate smooth coatings, dyeing, and control tack.
Applications of Wetting Agents
Use wetting agents when:
Paints & Coatings – to promote smooth application & even colored surfaces.
Agriculture – to promote even spreading of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers on leaf surfaces.
Textiles & Dyes – to improve penetration of dyes & color consistency.
Cleaning & Detergents – improve the performance of cleaning solutions.
Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics – to enhance active ingredient absorption.
Examples of Common Wetting & Dispersing Agents
To illustrate further, the following are some examples to consider:
Wetting Agents: Sodium lauryl sulfate – found in cleaning products and shampoos.
Alkylphenol ethoxylates – used in agriculture to help wet and promote even spreading of pesticides.
Dispersing Agents: Polyacrylates – used in paints and inks as dispersants for pigments.
Sodium polyphosphates – used in food products to disperse and stabilize mineral ingredients.
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)- used in drilling fluids to keep clay particles suspended.
It’s important to note that some additives can act as both wetting and dispersing agents, depending on their formulation and use.
Key Difference Between Dispersing Agent and Wetting Agent
While they both improve the interaction between liquids and solids, the main difference lies in what they improve:
| Feature | Dispersing Agent | Wetting Agent |
| Primary Function | Breaks up and stabilizes particles in a liquid | Reduces surface tension for better spreading and penetration |
| Main Goal | Prevents particle settling & agglomeration | Improves coverage & adhesion on surfaces |
| Application Focus | Maintaining suspension of solids | Enhancing liquid spread on solids |
| Examples | AMPS monomer, CMC, sodium polyphosphate | Sodium lauryl sulfate, alkylphenol ethoxylates |
Using Them Together in Industries
Many times, both agents are used together for the best results. For example:
In paints and coatings, A dispersing agent can keep pigments suspended evenly in a liquid, while a wetting agent will allow the paint to spread uniformly on the surface.
In textiles – A dispersing agent allows dyes to mix evenly so there are no lumps, while a wetting agent will help the dye wet and penetrate the fibers evenly.
In agriculture, A dispersing agent keeps the pesticide particles evenly suspended without lumping, while they wetting agent will help spread it across the surface of the plant.
Using these agents together will produce better results with your products and reduce waste for better efficiency while operating.
Choosing the Right Agent
The choice is all up to what you are trying to accomplish:
If you want solid particles to remain suspended evenly in an liquid for as long as possible without lumping, you would select a dispersing agent.
If you want a liquid to spread uniformly and adhere to a substrates surface, you would select a wetting agent.
Lastly, if you need both functions, you would need a formulation that will have both wetting and dispersing capabilities.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the difference between dispersing agent and wetting agent is important to any industry that deals with liquid-solid interactions.
Dispersing agents will keep particles suspended evenly, stop lumping, and improve stability of products.
Wetting agents help with spreading and penetrating surfaces like fabrics and skin for more uniform coverage and better adhesion.
In practice, industries often use both to achieve the best results. Whether you’re formulating paints, agricultural sprays, textiles, or pharmaceuticals, choosing the right additive can greatly improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance product performance.
In short, dispersing agents and wetting agents may work differently, but together they form the backbone of many high-quality industrial and consumer products, ensuring they perform just as intended from the first use to the last.
Sagar Telrandhe is a Construction Engineer with a B.Tech in Construction Engineering & Management. Passionate about infrastructure development, project planning, and sustainable construction, he specializes in modern construction techniques, project execution, and quality management, contributing to efficient and innovative building.