Precast concrete is a construction material that has revolutionized the way we build structures by providing fast, durable, and versatile options.
This blog will outline the uses, types, advantages, and some common applications of precast concrete in modern construction and discuss famous precast concrete buildings.
It shall also provide insights as to why precast concrete is the right choice for many construction projects. As with any good discussion, we will conclude with some frequently asked questions about this innovative construction material.
Table of Contents
What Is Precast Concrete?
Precast concrete refers to a variety of concrete items that are cast and cured under controlled conditions-typically at a factory or other off-site location, then brought to the construction site.
The precast elements are cast in molds that allow precise dimensioning in the manufacturing environment, thus improving the overall quality of the construction. Precast concrete can be used for numerous components, such as walls, beams, columns, floor slabs, and even for decorative innovations.
Precast has numerous advantages, including an increase in construction speed while mixing with concrete admixture. Regardless, while the precast elements are being made in a factory off-site, other operations on-site can take place simultaneously, minimizing the overall time taken for the actual erection.
Furthermore, better control of the quality due to adequate manufacturing conditions means that precast concrete elements are taught to be much stronger and to conform with bigger homogeny standards than those cast directly on-site.
Where Precast is Used?
Precast concrete finds application in various construction works with concrete admixture, from residential buildings to massive commercial and industrial projects.
It is especially selected for projects in which speed, quality, and durability are of primary concern. Multi-story buildings, highways, bridges, tunnels, and some infrastructure projects have used precast concrete elements.
Two chief advantages of precast concrete include the fact that it can be used for structural as well as non-structural features. Thus it provides flexible solutions for various architectural and engineering purposes.
Use of Precast Concrete in Frames
Modern construction jumps into the fight with precast concrete structures. Building frames are vertical and horizontal load-bearing members such as columns, beams, and slabs.
The usage of precast concrete gives the frame great strength and flexibility in design. Because they are being precast, structural components can be built concurrently with other activity, thus shortening construction time.
Also, precast concrete is designed with a view to aesthetic principles and purposes. The aesthetic can range from commercial to residential ventures.
Precast concrete frames find recognizes widest applicability in construction works where high structural safety is necessary, such as in commercial office structures, hospitals, and housing developments.
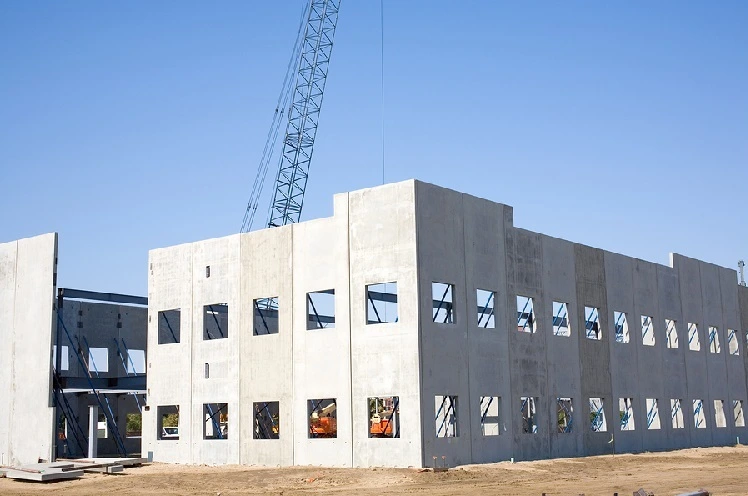

Use of Precast Concrete for Floors
Precast concrete in floor systems is most commonly used in multi-story buildings. Precast concrete slab floors are produced with various designs and sizes suitable for meeting the specifications of a building project. The floor components are then transported to the site, where they can be rapidly erected, greatly speedily.
The use of precast flooring systems provides for great quality control of all components processed in the controlled environments of factories. These floors enjoy great durability, increased overload-resistance, and fire-resistance.
Precast concrete floors are known to have some soundproofing properties, which make them an ideal choice for high-rise residential and commercial buildings.
Use of Precast Concrete in Cladding
Precast Concrete is the mainstay of building facades as a cladding material. Cladding is correlative to enhancing a building’s beauty and also protecting its frame from the effects of inclement weather.
With the application of precasting, the cladding panels contain the most variations in textures, finishes, and colors, making this method of design acceptable for modern and traditional use.
Precast concrete cladding is beautiful and functional as well. It has great insulating properties, which lowers heating and cooling costs, and is highly fire, wind, and stain-resistant.
Also, the panels can be designed so that they are relatively quick to install, thereby saving time and labor costs during construction.
In Which Type of Projects Can You Use Precast Concrete?
Precast concrete can be used in a wide spectrum of construction projects, from residential construction to commercial high-rises, bridges, and infrastructure projects. These applications include:
- Residential Buildings: Precast concrete is commonly used for the walls, floors, and even entire frames in multi-story apartments, townhouses, and single-family homes.
- Commercial and Office Buildings: Precast elements are frequently used in the construction of office buildings, hotels, and shopping centers, on account of speed, cost-effectiveness, and durability.
- Bridges and Infrastructure: Precast concrete is one of the ways in which bridges, tunnels, and roads are built due to its strength and capacity to carry tremendous weights.
- Industrial Factories: Factories, warehouses, and distribution facilities are all constructed using precast concrete components because of its strength and versatility.
What Are the Most Common Precast Products?
Precast concrete components are extensively used in modern-day construction, especially:
Precast concrete panels are used for constructing both internal and external walls; provide strength, durability, and aesthetics.
Precast concrete beams are used as a load-bearing horizontal member in building frames.
Precast concrete slabs: It is an excellent floor system to speed up the installation of load-bearing capacity installations.
Precast concrete columns: They are vertical elements that can carry very high loads.
Precast concrete stairs: Also popular for installing easy and quick multi-story buildings.
Precast concrete decking: Used on commercial buildings for roofing and floors.
Famous Precast Concrete Buildings
It cannot be overlooked that precast concrete has been used in its construction in some of the most notable buildings across the world, including:
The tallest building in the world, Burj- Khalifa in Dubai: A core wall, floor, and column of precast concrete are used in Burj- Khalifa tallest building in the world.
The Opera House of Sydney: Design of the famous Opera House makes use of both precast concrete and various other materials.

Space Needle of Seattle: This popular landmark Space Needle of Seattle uses precast concrete in the structural components of the building.
These structures amply demonstrate how precast concrete is used, besides forming functional buildings, to evoke an architectural marvel.
Related Post: The Ultimate Guide To Precast Concrete Walls in Construction
Why choose precast concrete?
The choice of precast concrete in construction projects thus provides,enumerated below, a number of advantages:
Time of construction is shortened: The precast elements are cast in a factory setting and limited on-site time expended.
This is cheaper than if reinforced concrete is used: Economically includes mixed structures resulting in higher initial investments but achieving a minimized expense in terms of labor costs, short cycles, and a long-term durability of precast concrete.
Strength and Durability: Precast concrete offers great flexibility in regard to construction materials as a result of its resistance to moisture, fire, and weather on the whole.
Design Flexibility: Precast elements may be shaped into any size, form, color, or finish imaginable, allowing a wide scope for architectural choice.
Sustainability: Precast concrete has durable qualities and can further be recycled, so it could contribute to a more sustainable construction process.
Conclusion
Precast concrete is the lifeblood of modern construction; hours of ease with the speed and strength it provides and extreme flexibility.
From structural frames, floors, and facades to infrastructure projects, precast concrete provides diverse benefits that make it an ideal choice for various types of buildings.
Its growing popularity in both residential and commercial projects continues to mark a remarkable turn in the future of building construction.
FAQS
When to use precast concrete?
Precast concrete, when quickness, quality, and durability are a priority, is used in, but not limited to, multi-story buildings, bridges, infrastructures, and residential projects.
Where is precast concrete used?
It is found in residential, commercial, industrial, and infrastructure construction, such as bridges and office blocks, and multi-story apartments.
What are the disadvantages of precast concrete?
On the other hand, the primary disadvantage is the high initial manufacturing and transport costs, although reduced labor and time for construction can offset these costs.
Does precast concrete crack?
Extreme conditions can make precast concrete crack, although proper design and quality control usually minimize the probability.
What is the lifespan of precast?
Typical lifespan of precast concrete is 50-100 years, depending on the environmental conditions and proper maintenance.
Is it more expensive to use precast?
Though precast concrete has a higher up-front cost in comparison to traditional poured-in-place concrete, its durability and cost-saving value over time in terms of labor makes it justified.
How do you maintain precast concrete?
Maintenance of precast concrete is pragmatic cleaning followed by a careful inspection for separation, cracks, or material loss and maintenance before deterioration sets in.
What is the maximum length of a precast panel?
A precast panel can be produced in any size, although the standard length is usually about 40 feet, which can, when transport allows, be increased to any arbitrary length.
Sagar Telrandhe is a Construction Engineer with a B.Tech in Construction Engineering & Management. Passionate about infrastructure development, project planning, and sustainable construction, he specializes in modern construction techniques, project execution, and quality management, contributing to efficient and innovative building.